
Timing Belt: The Best Tools for Tensioners
A car timing belt should always be checked when preventive maintenance is carried out, as it is essential to a vehicle operating normally.
As such, it is essential to know what it is and how this car system works to avoid unpleasant surprises resulting from a lack of maintenance.
Keep reading this article to learn how and when to change your car’s timing belt, the tools needed to replace it, how much it costs to change it, and much more.
![]()
- Open Ended Wrench: What are the best for your workshop?
What is a car Timing Belt?
Also known as a camshaft, a car’s timing belt is essential to ensuring an engine operates correctly.
Its primary function is to synchronise the movements of an engine’s moving parts to ensure that all intake and exhaust valves open and close in synchrony with the pistons.
How do Timing Belts work?
This system, which consists of a timing belt, tensioner, and water pump, connects the engine block to the cylinder head. In addition, it transmits the crankshaft‘s rotational movement to the camshaft, triggering the valves.
The system’s main purpose is to synchronise the four strokes of the engine, the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves, and the engine ignition (spark plugs or injectors in diesel engines).
The water pump pumps coolant, maintaining the engine temperature close to 90°C.
What is a car’s Timing Chain?
Timing chains are alternatives to timing belts, used in some vehicles and internal combustion engines.
The main difference is that while a timing belt is made of toothed rubber, timing chains are metal chains, though they operate similarly to belts.

What is a Timing Chain Tensioner?
A timing chain tensioner is essential in timing systems that use chains instead of belts to synchronise the moving parts of an engine.
Its primary function is maintaining the correct tension on a timing chain to ensure it remains engaged with the timing system gears.
What is the difference between a Manual Tensioner and an Automatic Tensioner?
What varies between these two systems is how belt tension is adjusted in a vehicle.
In a manual tensioner, belt tension is adjusted manually using tools that allow the tensioner to be adjusted. They are very common in old cars.
Where automatic tensioners are concerned, tension is adjusted automatically, as they have an internal mechanism that monitors belt tension and keeps it within the correct specifications.
How can you Check Belt Tensioner Wear?
To avoid belt failures and engine damage, you should perform regular checks by following these steps:
- Turn off the engine and allow it to cool;
- Locate the tensioners (usually inside the belt);
- Perform a visual examination – with a headlamp, if possible. In most cars, you won’t be able to see it without help from this tool.
If you notice cracks or wear on the tensioner pulley, it is a sign that you may need to replace either the belt, tensioner, or both components.
Noisy Belt Tensioner?
A tensioner becomes noisy when worn, damaged, or has problems operating. However, there may be other reasons behind it making a noise.
For example, if there is a gap, it is misaligned, or incorrectly tensioned, it can cause the belt tensioner to become noisy.
What is the Average Durability of a Belt Tensioner?
The lifespan of a belt tensioner varies from manufacturer to manufacturer. However, it will generally range between 100 thousand and 150 thousand kilometres.
How often you replace your vehicle’s belt tensioners depends on the instructions provided by your vehicle manufacturer.
When should you Replace your Timing Belt Tensioners?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing your timing belt every 100,000 to 150,000 kilometres or every 5 to 7 years, whichever comes first.
How much does an Alternator Belt Tensioner cost?
The price of an alternator belt tensioner varies depending on the type of vehicle, manufacturer, and its technical specifications. However, you can expect to pay between 20 and 80 euros.
What Risks do you Face in not Changing your Belt Tensioners in Time?
Failure to replace timing belt tensioners in time can have serious consequences on your vehicle’s engine, such as:
- Timing belt failure;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Loss of engine power and efficiency;
- Damage to the engine (bent valves, damaged pistons, or even needing to replace the engine).
Which tools do you Need to Change your Belt Tensioners?
To change your belt tensioners safely and efficiently, you’ll need the following tools:
- Headlamp;
- Ratchet wrench and box;
- Adjustable or open-ended wrench;
- Belt tension tool;
- Torque wrench;
- Engine locking tool.
In addition, you should wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles.
What are the Symptoms of a worn Timing Belt?
To find out if it’s time to replace your timing belt, pay attention to the following symptoms:
1. Physical Damage
One of the first signs of a broken timing belt is excessive wear or cracks on the toothed parts.
If there are lighter-coloured areas, it is a sign of misalignment or incorrect tension.
2. Noise in the engine
Timing belt noise is an uncommon symptom. However, do not ignore it if you hear it.
What happens if you do not change your car’s Timing Belt?
If you choose not to change your car’s timing belt within the period recommended by the vehicle manufacturer, you risk it wearing out or snapping.
This could seriously damage the engine, leading to the valves colliding with the pistons, requiring expensive repairs.

After how many kilometres should the timing belt be changed?
You should generally travel 100,000/120,000 km before changing your car’s timing belt. You should change it every 5 years if you don’t drive often.
You should always, however, change your car’s timing belt whenever you detect an anomaly. When doing so, you should also consider changing the tensioner.
How do you Change a Timing Belt?
Though knowing how to replace a timing belt is important, its execution should be done by qualified professionals only.
A timing belt kit is required for a replacement.
What is a Timing Belt Kit?
As the name implies, it is a kit that includes all the parts necessary to replace a timing belt, including:
- A belt;
- Tensors;
- Water pump.
Which tools do you Need to Change a Timing Belt?
The KROFtools catalogue contains the following tools that can be used to change this component, though the application of each product may vary from car to car.
Universal Tensioning Gauge for Cam Belts

This gauge is used prior to adjusting a timing belt by measuring the tension in Nm.
It can be used on belts of different thicknesses. For belts with a thickness of more than 5mm, see the table on the product datasheet.
Click on the image to find out more about our Universal Tensioning Gauge for Cam Belts (Ref. 2899).
Tool for Belt Tension
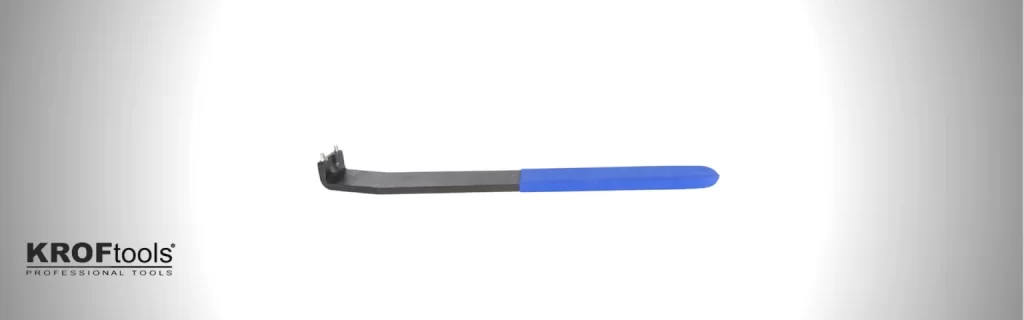
This two-pin wrench is suitable for use on VAG diesel group vehicles such as the Volkswagen Lupo 3L 1.2 TDI. It is also compatible with the Seat Alhambra 2.0.
Click on the image to find out more about our Tool For Belt Tension (Ref. 1575).
Tensioner for Timing Belt Installation
- Tension Lever For Ribbed Bel Installation (Ref. 2898) – compatible with VAG models: ASN, BBJ, VW Golf, VW Passat, VW Polo, VW T4;

- Timming Chain Tensioner Lever OEM C416 (Ref. 1657B) – compatible with Fiat/OPEL/FORD 1.3 DIESEL Lock Out Kit (Ref. 1657).

How much does a Timing Belt cost?
The price of a timing belt kit generally ranges from 50 to 100 euros.
How Much Does it Cost to change a Timing Belt?
What each repair shop charges for labour will vary greatly. As such, and depending on the car, the price of changing a timing belt can vary between 200 and 1000 euros.
Interested in finding out more about the world of all-things cars? Then follow us on Facebook and keep up with our daily content.
![]()
